Chaos, complexity, curiosity and database systems. A place where research meets industry
Monday, 30 July 2018
Systems | Fueling future disruptions
It is an exciting time of year with so many informative and knowledge sharing conferences from Google to Microsoft. It is the 2 day Microsoft Faculty Summit 2018, 1 - 2 August 2018. This brings together leaders and researchers from the broad systems research area in computer science. Systems research is the foundation innovation grows from. It has the potential to disrupt the future.
The conference guide can be downloaded
Saturday, 28 July 2018
What is Best Practice?
Best practice is a pervasive term that means different
things to different people. Best practice has been defined in various ways (Dembowski 2013; Wellstein & Kieser 2011; Sanwal
2008).
Dani et al. (2006) stipulate “A best practice is
simply a process or a methodology that represents the most effective way of
achieving a specific objective”. Jarrar &
Zairi (2000) state that the term best practice is
often used within organizations to depict leadership and is recognised as the
best way to achieve superior results. In
the glossary of benchmarking terms (American
Productivity and Quality Centre 1999) cited in (Jarrar &
Zairi 2000, p.S734)
best practices were defined “Those practices that have been shown to
produce superior results; selected by a systematic process; and judged as
exemplary, good, or successfully demonstrated. Best practices are then adapted
to a particular organisation”. Many different situations require
different best practices and with new technology evolving ‘best’ is a moving
target (Jarrar & Zairi 2000).
Markus (2011, p.4) argued
that the cultures and practices that develop over time in organizations have
changed to become “off-the-shelf” services labelled best practice standards,
which organizations needed to adopt and understand. Markus argued the change
from unique coded management ideas for handling packages to standard software
with relentless upgrades requires knowledge development and standard practices.
Sanwell (2008) stated that the use of best
practices are affected by certain beliefs:
- Best practices help make decisions quickly in a complex uncertain world.
- Best practices are easier because they have been proven by other organizations who also operate with complex and uncertain elements.
- Management understanding of other organizations in the field are organizational specific. Best practices are often developed later and often already behind leading organizations.
- Value must be gained from best practices as other experts, consultants and vendors share them for current trends.
- Best practices can improve performance.
Falconer (2010) argued to the contrary that
best practice exacerbates failure:
“Best practice is flawed because it acts as a placeholder for
proper management practice, displacing accountability for effectiveness and
fit. Best practice is flawed, further, because it supplants strategy, adopting
solutions out of convenience or copying them reactively, and supplants
innovation, allowing “the best we know about”, “the best we’ve come across”, or
even “the best we’ve done before” to be adequate. Best practice considers the
world predictable, and discounts the emergence of better, novel ideas” (Falconer 2010, p.754)
Falconer thought that problem situations are being
incorrectly handled due to best practices replacing analysis.
Sanwell (2008) pointed out that changing
these best practices in the multidimensional world requires consideration of
organizational culture and behaviour, organization processes and organizational
systems. As Gonnering
stated,
“Best Practices” can serve as a beginning but adaptation
will most likely be necessary. Outcome is an emergent property, and the
organization that has taken the time to learn the methodology of improvement
will reap the benefits. The “continuous” in “continuous quality improvement”
depends upon rapid-cycle, small-scale serial innovation and not a static and
dogmatic adherence to past processes.” (2011, p.100)
Gonnering argued that complex problems
using best practices failed to have positive outcomes and forced the complex
systems to become chaotic. Bretschneider et
al. (2004) highlighted three important
characteristics of best practice: a comparative process, with action, and
linked to an outcome or goal. Nattermann (2000) suggested best practice might
be the most widely used management tool in business and important for improving
operational efficiency, but for strategic decision making, best practices might
not be the best way forward to increase profit margins. Best practices
management could be used to benchmark performance, with certain benchmarks being
required to demonstrate best practices.
The core or classic best practices utilised within the
database community have been developed through the sharing of knowledge,
experience and actual outcomes across the sector. The improvement of these best
practices were raised by Gratton & Ghoshal
(2005) with the term “a signature
process”, a process that envelops the company’s character and idiosyncratic
nature. This signature process could advance the company although it required
careful adaptation and alignment to business goals to succeed. However the
allure of classic best practices that were clear, logical and easy to
understand were the ones shared within the database community, the body of
knowledge often yielding optimal results (Tucker et al.
2007).
Some best practices were tightly coupled with their organizations and
inseparable from the context (Becker 2004).
Jarrar & Zairi (2000) identified three types of
best practice: proven best practice across organizations, good practice
techniques for an organization, and unproven good ideas based on intuition. There
were drawbacks with unproven ideas that could be a matter of luck and the lack
of information to reduce the risk, lack of situational context, application criteria
or success measure (Falconer 2011). This serendipitous discovery
could lead to ease of deployment and innovation.
The Cynefin framework (Snowden & Boone 2007) classified and ordered simple
systems in the domain of best practices. In an earlier paper in the chaos domain Kurtz & Snowden (2003) argued that applying best practices
probably caused the chaos in the first place. They argued that different
contexts use different management responses and that there are different tools
for the management of complex contexts. The best practices domain is based on
cause and effect relationships that have simple contexts, often within areas
that do not change frequently.
Wagner and Newell (2011, p.400) stated that “The best way of
operationalizing a process in one context and at one point in time may be
different in another context and time”. They contended that there is no such
thing as best practice, as knowledge is created by engagement in a practice.
Practice is always changing and emergent with inconsistencies in the same
practice, with best practice being defined locally.
Wagner and Newell (2011, p.401) suggested
a move to negotiated practice with a cooperative approach to best practice
adoption. Their aim was to smooth out complex implementation through
compromise. They concluded that highlighting problems with identifying best
practice (due to it being an interactive process based on learning through implementation
with information systems) sometimes required customisation to work well. This
approach was also adopted by Avgerou & Land
(1992) with their notion of
‘appropriate’ context specific practice, where information systems innovation
looked for “best practice, or suitable new organizational form for the
information age” (Avgerou 2011, p.650).
Avgerou drew together organizational and information
systems to develop a framework which had one key tenet of a knowledge
management system or a best practice solution to help address static and
commoditized technology.
Best practices and procedures were continually developed by
database software providers (e.g. Microsoft, Oracle and MongoDB) to enable the management
of database systems to be carried out to the highest standards. The procedures
were based on formal rules the business world defined which were sometimes
called standard operating procedures (Becker 2004). Best practices were defined
by the software providers as exemplary tested designs for certain
configurations or ways of doing things. They were multi-faceted and resided in
varying layers from architectural design, through development, to operational
management.
The management of database systems utilizes best practices
and procedures provided by software providers and often industry best practices
shared by the community. McGregor (2007) argued that this rarely leads
to great customer service. McGregor’s (2007) idea that “Next Practice” was
the future of continually analysing and looking for positive quality products
and service in other organizations, would bring ideas and innovation to improve
the business. There was an aspiration to improve database management and
improve business processes to provide good quality service when managing IT
projects and database systems. Best practices might not however be the best
solution. Sanwell (2008) raised some key issues with
using processes and strategies created by other organizations, and did not
believe that following these would create a better organization or bring about
improvement.
Within database systems there are various types of
practices and procedures that need to be incorporated within change processes.
Savage (2014, p.17) stated Stonebraker thought “in
memory” database engines will take over online transactional processing systems
(OLTP). Savage (2014, p.16) shared Stonebraker’s views on
the database world, that it could be divided into three types: OLTP, data
warehouses and everything else (Hadoop, graph databases). This was likely to
mean three or more database management and best practices models were required.
Best practices operate at different levels within the
sphere of database management. There are technology best practices which deal
with specific tasks for deployment of databases onto servers or into the cloud;
and management best practices which relate to higher level functions and
overall processes. In addition there are best practices which are defined by
software vendors for their own products.
As technology and management change, in the world market, and more is
understood about certain areas, best practices change. Thus best practices are
replaced with new best practices. The large collection of best practices
created are likely to be defined and owned by a multitude of people. This can
cause problems with conflicting best practices. Sometimes there is a mismatch between
best practices and a compromise needs to be found where possible.
Best practices are intended to be useful for technical
solutions to help people provide the required results. They aim to provide a
useful guide on what management need to do to perform certain tasks. Best
practices are sometimes adapted from vendor or industry defined best practices
for nonstandard configurations or different business scenarios. However, sometimes
communication is lacking between the management requirements, the vendors’
practices and the technology tasks. Different teams may each create best
practice, in places where the technology overlaps, which are not shared. There
are therefore limitations to the usage of best practices. The best practices
presented are significantly different for ILTM, CMM and ILTIL. There are many different types of
tasks from in depth technical ones to higher level models that combined can
produce a well-managed database system. Each task, model or part of the
database system will have its own best practice, which aims to achieve those
reliable results. These best practices at different levels may, in practice,
sometimes be in conflict. This discussion on best practice has shown there are
many diverse views on the usability and definition of best practice. The
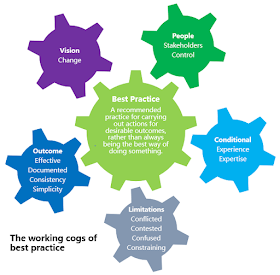
working definition in my research (Holt, 2017) for best practice was: a recommended practice
for carrying out actions for desirable outcomes, rather than always being the
best way of doing something. The research best practice findings are in Holt et al. (2015) and the working cogs of best practice summaries the findings.
American
Productivity and Quality Centre. (1999). What is benchmarking. Retrieved from www.Apqc.org
Avgerou,
C. (2011). Discources on innovation and development in information systems in
developing countried research. In R. D. Galliers & W. L. Currie (Eds.), The
Oxford Handbook of Management Information Systems (p. 650). Oxford: Oxford
University Press.
Avgerou,
C., & Land, F. (1992). Examining the appropriateness of information
technology. In S. Odedra & M. Bhatnagar (Eds.), Social Implications of
computers in developing countries (pp. 26–42). New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill.
Becker,
M. C. (2004). Organizational routines: a review of the literature. Industrial
and Corporate Change, 13(4), 643–678.
https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/dth026
Bretschneider,
S. (2004). “Best Practices” Research: A Methodological Guide for the Perplexed.
Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 15(2), 307–323.
https://doi.org/10.1093/jopart/mui017
Dani,
S., Harding, J. a, Case, K., Young, R. I. M., Cochrane, S., Gao, J., &
Baxter, D. (2006). A methodology for best practice knowledge management. Proceedings
of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering
Manufacture, 220(10), 1717–1728.
https://doi.org/10.1243/09544054JEM651
Dembowski,
F. L. (2013). The Roles of Benchmarking , Best Practices & Innovation in
Organizational Effectiveness. International Journal of Organizational
Innovation, 5(3), 6–20.
Erica
Wagner, & Newell, S. (2011). Changing the story surrounding enterprise
systems to improve our understanding of what makes erp work in organizations.
In R. D. Galliers & W. L. Currie (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of
Management Information Systems (p. 401). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Falconer,
J. (2010). “Best Practice” as Worst Practice : Broken Metaphor , Nude Emperor. Proceedings
of the European Conference on Intellectual Capital, 754–762.
Falconer,
J. (2011). Knowledge as Cheating : A Metaphorical Analysis of the Concept of “Best
Practice.” Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 180, 170–181.
https://doi.org/10.1002/sres
Gonnering,
R. S. (2011). The Seductive Allure Of “Best Practices”: Improved Outcome Is A
Delicate Dance Between Structure And Process. E-CO, 13(4), 94–101.
Gratton,
L., & Ghoshal, S. (2005). Beyond Best Practice. MITSloan Management
Review, 46(3).
Holt, V. et al. (2015) ‘The usage of best practices and procedures in the database community’, Information Systems, 49. doi: 10.1016/j.is.2014.12.004.
Holt, V. (2017) A Study into Best Practices and Procedures used in the Management of Database Systems. The Open University. Available at: http://oro.open.ac.uk/id/eprint/50950.
Jarrar,
Y. F., & Zairi, M. (2000). Best practice transfer for future
competitiveness: A study of best practices. Total Quality Management, 11(4–6),
734–740. https://doi.org/10.1080/09544120050008147
Kurtz,
C. F., & Snowden, D. J. (2003). The new dynamics of strategy : Sense-making
in a complex and complicated world. IBM Systems Journal, 42(3).
https://doi.org/10.1147/sj.423.0462
Markus,
M. L. (2011). Historical Reflections on the Practice of Information Management
and Implications for the field of MIS. In R. D. Galliers & W. L. Currie
(Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Management Information Systems (pp. 3–15).
Oxford: Oxford University Press.
https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199580583.003.0002
McGregor,
M. (2007). When Best Practice is Just Not Good Enough Why and How You Need to
be Better than the Best. BPTrends, (July), 1–2.
Nattermann,
P. M. (2000). Best practice does not equal best strategy. The McKinsey
Quarterly, 2.
Sanwal,
A. (2008). The Myth of Best Practices. Journal of Corporate Accounting &
Finance, 19(5), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcaf
Savage,
N. (2014). The Power of Memory. Communications of the ACM, 57(9),
15–17. https://doi.org/10.1145/2641229
Snowden,
D. J., & Boone, M. E. (2007). A Leader’s Framework for Decision Making. Harvard
Business Review, 85(11), 68–76.
Tucker,
A. L., Nembhard, I. M., & Edmondson, A. C. (2007). Implementing New
Practices: An Empirical Study of Organizational Learning in Hospital Intensive
Care Units. Management Science, 53(6), 894–907.
https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1060.0692
Wellstein,
B., & Kieser, a. (2011). Trading “best
practices”--a good practice? Industrial and Corporate Change, 20(3),
683–719. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/dtr011
Friday, 20 July 2018
Inspire 2018 - Intelligent Cloud and Edge
Inspire 2018 is in Las Vegas, Nevada, 15-19 July. This is the Microsoft premier event for partners. It has been interesting to see the discussions on Twitter during Inspire. These three quotes sum up a possible future state.
Without data, AI doesn't work. Data is the fuel for any AI service @TimNilmaa
It is our collective objective to democratize AI in every industry @Microsoft
The era of the intelligent edge has three defining characteristics AI, ubiquitous computing and people centred experiences @Microsoft
These three areas tie in with the Satya Nadella book 'Hit Refresh' that I have been reading. It is a truly extraordinary book that inspires you to innovate and use that innovation for a better future.
I found in my own research, people centered experiences, drive much of what, where and how things are achieved. It is these small differences in inputs, that have the possibility to change the outputs in such variable ways. This leads to an expanding complex environment. But what if you could understand that complexity and adjust the tasks that need to be carried out in diverse cross disciplinary teams by building in AI and using a CODEX (Control Of Data EXpediently) model, when managing data and database systems. The result would stretch the breadth and depth, from on premises to cloud delivery, incorporating current and future states. A fully autonomous aid to managing data and database systems using the CODEX that is described my research should help gain that intelligent edge.
Wednesday, 18 July 2018
Wednesday, 11 July 2018
Microsoft Research Open Data Sets
Microsoft Research Outreach team worked with the community to enable adoption of cloud based research. As a result they have launched Microsoft Research Open Data, a new data repository for the global research community. Microsoft wish to bring processing to the data rather than rely on data movement through the internet. This useful addition allows the data sets to be copied directly to the Azure based Data Science virtual machines. More details can be read here. The aim is to provide anonymized curated and meaningful datasets that are findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable. This follows on from the data-intensive science fourth paradigm of discovery discussed by Jim Gray.
The open data set categories can be seen below.
Saturday, 7 July 2018
The Future State - Serendipitous Data Management
Gone are the days where companies can survive on existing products
and services. The need to continually innovate to stay ahead in a fluid world,
requires a change in direction. Many articles have been written, in both
academic research and Industry, to try to predict what will be the future state
of data technology and what will be this year's trends.
Currently research meets industry in a rebirth of industry-based
research teams consisting of organisational only teams or industry
collaborating with universities. Guzdial shares his thoughts in the Communicationsof ACM March 2018 journal that "for the majority of new computer science
PhD's, the research environment in industry is currently more attractive".
Particularly the need within industry to continually innovate cries out for
more research divisions in industry. Part of this change is due to the rapid
expansion of emerging technology but also the realization, of what data science
and artificial intelligence (AI) can add to a business. Data science requires
collaboration between people, teams and organisations as interdisciplinary
skills are needed to solve today’s problems.
There is an emerging trend whereby more research institutes have
been created or existing ones hiring more staff. Microsoft have created a new
organization, Microsoft Research AI (MSR AI), to pursue game-changing advances
in artificial intelligence. The research team combines advances in machine
learning with innovations in language and dialog, human computer interaction,
and computer vision to solve some of the toughest challenges in AI.
AI machine learning intelligence, based on big data, is a complex
problem to solve, to empower people for the future. In the current world there
is the need for collaboration. Greengard in the Communications of ACM March 2018
journal, raised a concern that "mountains of data produce incremental
gains, and coordinating all the research groups and silos is a complex
endeavour". Managing data is
complex and the key areas that I think will define the next revolution are in
the graph.
Telling stories from the data is increasingly important in this ever-changing
holistic environment. Skills need to be developed in this area as communicating
the meaning of data is crucial. Aiming for improvement in business, science,
robotics, space and health can initially appear through intelligent automation
and can produce further actionable insights.
Data visualization is a key component to telling the story and
seeing anomalies. Parameswaran discussed at SIGMOD 2018, that it is the scale
that brings databases and visualisation together. He highlighted two problem
areas, too many tuples and too many visualisations. It is an interesting point
to consider how to address the excessive data points and how to appropriately
find the right visualization for the data, to gain insight at speed.
Innovation is key to the next step. I believe that is by making
beneficial discoveries by design through scientific experiments from quality
data in a continuous and autonomous fashion. I call this Serendipitous Data Management. This improvement and innovation will
come from having sound practices for big data management that enable actionable
data insights at speed.
Another trend I am seeing in research and industry is looking at
how data is processed in centralised data lakes and moving that processing to
the edge, particularly for IOT at the moment. As well as this increasing
security, if the data can remain at source, it also reduces the volume of data
transit which is currently unsustainable. How to consolidate these distributed
data sources and produce analysis across disparate systems is an interesting
challenge to solve. In conclusion the system built on data creates a rapidly
changing landscape of which I see as the key components in defining
revolutionary changes to society and culture.
Thursday, 5 July 2018
2018 MVP Reactions
Peter Laker published an article about reactions from the 2018's NEWEST Most Valuable Professional (MVP) award winners. What a great set of reactions from some amazing people.
Privileged to have my comment listed on the reactions list.
Privileged to have my comment listed on the reactions list.
Sunday, 1 July 2018
Tutorial on Tree Based Modeling
I found a useful tutorial on tree based learning
The tutorial includes
The tutorial includes
- What is a Decision Tree? How does it work?
- Regression Trees vs Classification Trees
- How does a tree decide where to split?
- What are the key parameters of model building and how can we avoid over-fitting in decision trees?
- Are tree based models better than linear models?
- Working with Decision Trees in R and Python
- What are the ensemble methods of trees based model?
- What is Bagging? How does it work?
- What is Random Forest ? How does it work?
- What is Boosting ? How does it work?
- Which is more powerful: GBM or Xgboost?
- Working with GBM in R and Python
- Working with Xgboost in R and Python
- Where to Practice ?